[Structural Institute]
Shan Wang, Jun Peng, Shao-Bo Kang. Evaluation of Compressive Arch Action of Reinforced Concrete Beams and Development of Design Method. Engineering Structures, 2019, 191, 479-492
Keywords: Reinforced concrete beams, Compressive arch action, Analytical model, Tension-stiffening effect, Slip of tensile reinforcement, Simplified design method
High Lights:
An analytical model is developed for compressive arch action in reinforced concrete beams, in which the tension-stiffening and slip of reinforcement is considered.
A simplified method is derived in accordance with equilibrium and compatibility and can be used in design.
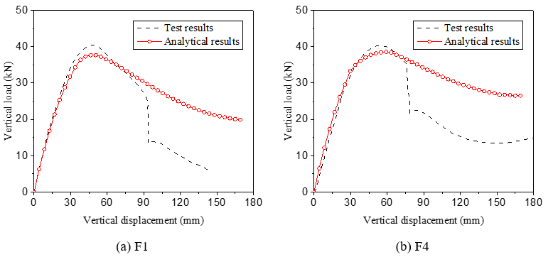
Comparisons with test data and other models suggest that the design method yields good estimations of compressive arch action.
Abstract:
This paper describes a study on the compressive arch action of reinforced concrete beams with various levels of horizontal restraints. An analytical model is proposed based on Park’s assumption, in which the tension-stiffening effect of steel reinforcement and its slip relative to beam-column joints are considered. The model is calibrated by experimental results of beam-column sub-assemblages and frames subject to column removal scenarios. The model is calibrated by experimental results of beam-column sub-assemblages and frames subjected to middle column removal scenarios. A parametric study is conducted to shed light on the effects of horizontal restraints on the axial compression force of beams and the strain of compressive reinforcement. Analytical results suggest that the compressive reinforcement may not yield under compressive arch action, and its strain varies with the axial compression force in the beam. To develop a simplified design method, the relationship between the axial compression force and the strain of compressive reinforcement is established through the theoretical axial force-bending moment interaction diagram. An explicit expression for axial compressive strain is derived from force equilibrium and compatibility and incorporated in the design method to evaluate the compressive arch action capacity and associated axial compression force of reinforced concrete beams. Comparisons with existing experimental results in the available literature and other models suggest that the design method yields reasonably accurate estimations of critical parameters related to compressive arch action.
Resource:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0141029619306819