[Clean Energy]
Jin C Q, Bai X L, An Y N, et al. Case study regarding the thermal environment and energy efficiency of raised-floor and row-based cooling [J]. Building and Environment, 2020, 182:107110.
Keywords: Thermal environment; Energy efficiency; Raised-floor cooling; Row-based cooling; Data center
High Lights:
Experimentally investigates the thermal environment and energy consumption of a data room.
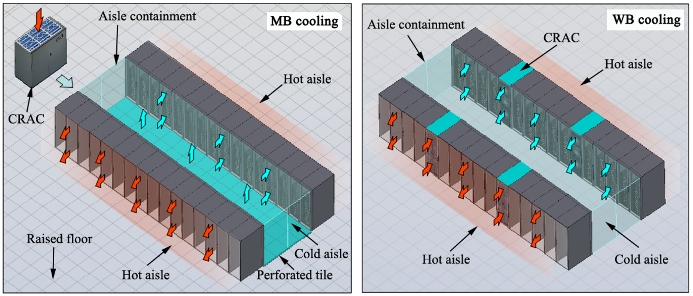
Compares the thermal and energy characteristics between raised-floor and row-based cooling.
Row-based cooling provides better performance vs. raised-floor cooling.
Some problems of the application of the row-based cooling are found.
An index is proposed to evaluate the degree of the interaction between different modules.
Abstract:
Data centers are energy-intensive facilities, and their thermal environment and energy efficiency are key research areas. In this study, the airflow distribution and energy consumption of a campus data room were experimentally investigated, and the results pertaining to raised-floor (before retrofitting) and row-based (after retrofitting) cooling were compared. The thermal environment was evaluated in terms of the rack cooling index (RCI), return temperature index (RTI) and supply heat index (SHI), and the energy efficiency was estimated using the power usage effectiveness (PUE) and mechanical load component (MLC). The results indicated that row-based cooling corresponded to a better thermal environment and higher energy efficiency compared with those of raised-floor cooling. The SHI decreased from 0.79 to 0.31, and the difference in the PUE and MLC values before and after retrofitting was 0.27 and 0.14, respectively. These benefits can translate into a total energy saving of 110,829 kWh per year. However, row-based cooling involves certain limitations, such as the presence of vortexing airflow, uneven air supply temperature, and interaction among different modules, which must be further examined. This paper proposes an index that can be used to evaluate the interaction among different modules.
Resource:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0360132320304856