[Structural engineering]
Shuangshuang Jin, Jiulin Bai , Experimental investigation of buckling-restrained steel plate shear walls with inclined-slots .Journal of Constructional Steel Research 155 (2019) 144–156 .
Keywords: Energy dissipation device Steel plate shear wall (SPSW) Buckling-restrained;Inclined slots;Hysteretic behavior Quasi-cyclic test
High Lights:
Three half-scale specimens were fabricated and tested under quasi-static cyclic loading.
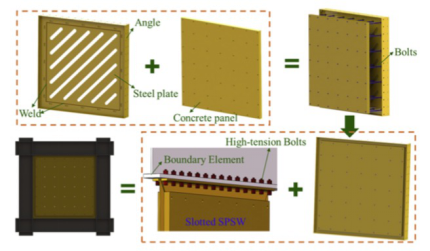
Details for proper fabrication of the slotted SPSW were configured.
The slotted SPSW is capable of providing high lateral force-resisting and energy dissipation.
Abstract:
A buckling-restrained steel plate shear wall with inclined slots (simply referred as “slotted SPSW”) consisting of an inner steel plate sandwiched between two precast concrete panels, has been developed as an energy dissipation device of structures. The steel strips between inclined slots behave like a series of buckling-restrained braces to dissipate the energy through inelastic axial deformation when subjected to cyclic loading. This paper experimentally investigated the seismic behavior of slotted SPSWs. Three half-scale specimens were fabricated and tested under quasi-static cyclic loading. Details for proper fabrication of slotted SPSWs were firstly configured. The results illustrated that the slotted SPSW could sustain the target lateral drift ratio (2%) without a reduction of shear force and energy dissipation capacity. Moreover, the tested specimens exhibited stable fatigue hysteresis loops when the cyclic loadings were repeated 30 times at 1.5% peak lateral drift ratio. The maximum drift ratio of tested specimens reached 3.5%, and the cumulative plastic ductility factor was larger than 200. The experimental results indicate that the slotted SPSW is capable of providing high lateral force-resisting and energy dissipation, which can be widely used in engineering structures.
Resource:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2018.12.021