Xiao Yang, Nan Bowen, McCartney John S.. Thermal Conductivity of Sand–Tire Shred Mixtures[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2019, 145(11): 06019012.
Keywords: Thermal conductivity; Sand–tire shred mixtures; Relative size ratio; Volumetric mixing ratio; Empirical model
High Lights:
Abstract:
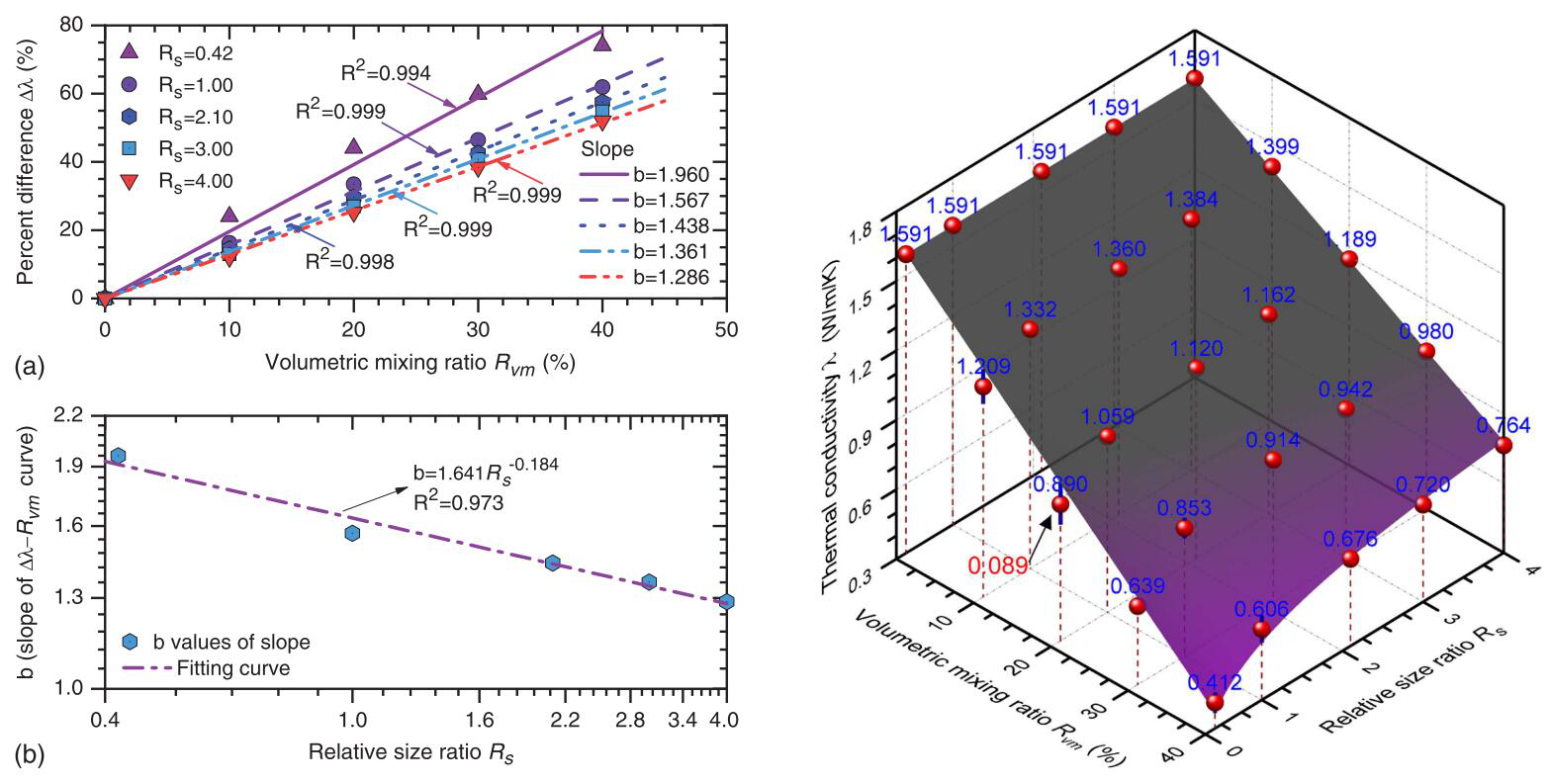
Sand–tire shred mixtures are useful as thermal backfills due to their lower unit weight and thermal conductivity than those of most soils. In this study, a series of thermal conductivity tests on sand–tire shred mixtures and pure sand were performed to investigate the effects of volumetric mixing ratio and tire shred particle size. A volumetric mixing ratio of 40% was found to yield the greatest decrease in thermal conductivity from that of pure sand, with a maximum percentage difference of 72%. Using tire shreds with a larger relative size ratio was found to result in higher thermal conductivity, and the maximum variation in the thermal conductivity percentage difference with the relative size ratio reached about 20% at a volumetric mixing ratio of 40%. An empirical model proposed to predict of the thermal conductivity of quartz sand–tire shred mixtures captured trends in the experimental data.
Resource:https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0002155