[Underground Engineering]
Xianshan Liu⁎, Ming Xu, Pengwei Qin. Joints and confining stress influencing on rock fragmentation with double disc cutters in the mixed ground[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2019,83:461-474
Keywords: Mixed ground, 3-D discrete element model, Double disc cutters, TBM
Fragmentation mechanism
Abstract:
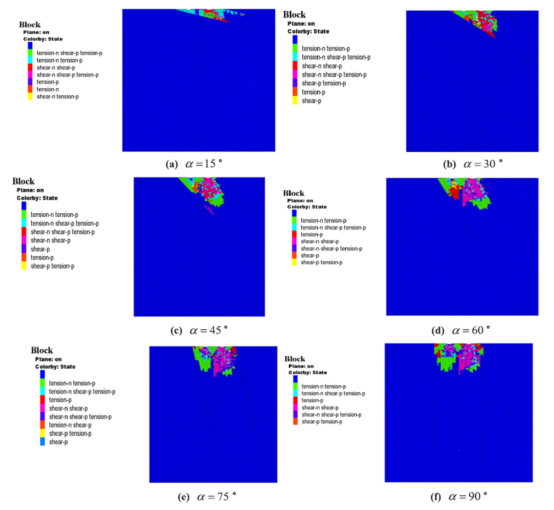
Complex geological factures are often encountered in the tunneling boring machine (TBM) excavation leading to many serious problems, especially the mixed ground conditions involving in the different geological properties should be paid more attention. To better investigate the effects of the mixed ground characteristics on rock fragmentation process by double TBM cutters, the model embedded crack propagation algorithm combined with M-C failure criterion has been calibrated for the mixed ground by double disc cutters. And then, the cutting simulations are conducted by 3DEC considering joint spacing, joint orientation and confining stress. The results under different conditions indicate that smaller joint spacing implying weaker properties favorably cause more cracks initiation and propagation by double cutters, and the cracks are tending to propagate along the joint plane and facilitate the rock chips beneath the cutters. And it is found that the joints are inclined to the soft rocks, more shear failure induces more cracks propagating inside the soft rocks, indicating that these rocks can be fragmented more completely. Meanwhile, with the increase of confining stress, rock fragmentation is more difficult resulting in the decrease of the cutting efficiency, especially the cracks induced by shear failure in soft rocks propagating along the free surface and interface cannot link the minor cracks by tensile failure in hard rocks to form rock chips. Furthermore, as noted from the variation of fragmentation load and specific energy under different conditions, smaller joints spacing causes smaller fragmentation load and specific energy to improve the cutting efficiency, however, greater confining stress gives more restrain for the cracks propagation, and the rock chips cannot effectively form between two types of rocks, resulting in lower fragmentation efficiency. And in addition, the optimal cutter spacing has also been analyzed under above conditions, which helps to provide appropriate measures for improvement of rock fragmentation efficiency and TBM performance during the TBM
excavation process.
Resource:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2018.08.051